Epithalon (Anti-Aging) 10mg/vial
$40.00
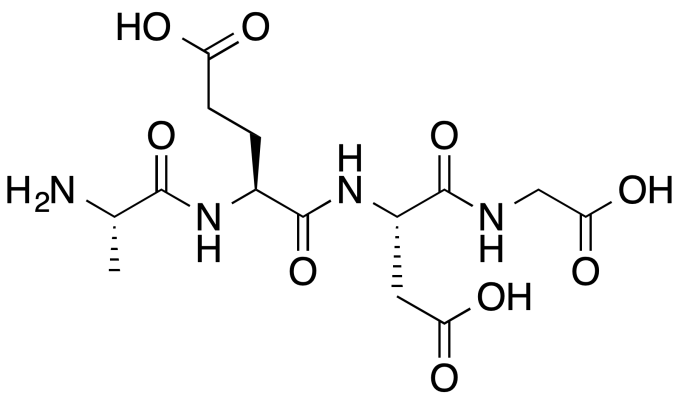
is a combination of 4 amino acids also known as AGAG. It is a relatively new drug (discovered over 30 years ago in animals brain), but it has already proven its convenience of use and having stunning effects like:
- Healing of damaged and decaying muscle cells;
- Life quality and length improvements;
- Lower possibility of severe diseases occurrence like cancer;
- Energy levels enhancement;
- Sleep normalization.
Epithalon also has premium quality, which is proven by Apoxar`s marks and quality certificate by independent party lab test.
Brand: Apoxar
Substance: HGH & Peptides
Dosage and packing: 10mg per vial, 1 vial
The Aging Breakthrough
Aging research has entered a revolutionary phase, and Epithalon stands at the forefront of this scientific exploration. This synthetic tetrapeptide, mimicking the natural pineal gland peptide Epithalamin, potentially influences one of biology’s most fundamental processes: cellular senescence. Researchers globally now investigate how this simple four-amino-acid compound might extend telomere length and modulate aging mechanisms.
Unlike many anti-aging supplements, Epithalon operates at the epigenetic level, potentially addressing aging’s root causes rather than merely treating symptoms. This comprehensive guide examines the peptide’s science, research findings, potential applications, and current status in longevity medicine.
1. Understanding Epithalon: Molecular Structure and Origins
Epithalon (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) represents a synthetic version of the pineal peptide Epithalamin. Russian scientist Vladimir Khavinson first identified the original peptide during decades of pineal gland research. His team discovered that pineal extracts could extend lifespan in animal models, eventually isolating and synthesizing the active component.
The peptide’s simplicity belies its potential complexity of action. With just four amino acids—alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine—Epithalon demonstrates remarkable bioavailability and cellular penetration. Researchers believe its small size enables efficient crossing of cellular and blood-brain barriers, facilitating systemic effects from a minimal molecular framework.
2. The Telomere Connection: Epithalon’s Proposed Mechanism
Telomeres, the protective caps at chromosome ends, naturally shorten with each cellular division. This shortening serves as a primary biological clock, triggering cellular senescence when telomeres reach a critical length. Epithalon research suggests the peptide may activate telomerase, the enzyme responsible for telomere maintenance and extension.
Studies, primarily in animal models and cell cultures, indicate Epithalon administration correlates with increased telomerase activity. This potential telomerase stimulation could theoretically slow, halt, or even reverse telomere shortening—a groundbreaking proposition in aging intervention. The peptide may accomplish this through epigenetic regulation, potentially influencing gene expression related to telomerase production without directly altering genetic code.
3. Research Findings: Animal Studies and Cellular Models

Scientific literature reveals compelling, though preliminary, findings:
-
Rodent longevity studies show lifespan extension up to 25-40% in some models
-
Cellular research demonstrates reduced senescence markers in fibroblast cultures
-
Reproductive system studies indicate restored estrous cycles in aged rodents
-
Melatonin regulation research suggests pineal gland function modulation
A pivotal study published in Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine demonstrated that Epithalon administration increased telomerase activity in human cell cultures. Another research series noted improved immunological parameters in elderly patients receiving pineal peptides. However, the scientific community emphasizes these findings require large-scale human validation.
4. Potential Benefits and Applications in Research
Current investigation focuses on several potential applications:
-
Cellular rejuvenation research – Examining effects on senescent cell clearance
-
Age-related disease models – Studying impact on conditions with accelerated aging components
-
Cognitive aging studies – Investigating potential neuroprotective properties
-
Reproductive aging research – Exploring effects on age-related fertility decline
Researchers emphasize that these areas represent investigational pathways rather than established medical applications. The peptide’s potential multi-system effects make it a valuable tool for understanding interconnected aging processes.
5. Epithalon vs. Other Peptides: Comparative Analysis
The peptide landscape includes several compounds with overlapping but distinct profiles:
Epithalon vs. Thymalin: While both are Khavinson peptides, Thymalin primarily targets immune system modulation, whereas Epithalon focuses on telomere and epigenetic regulation.
Epithalon vs. TA-65: Both target telomerase, but TA-65 derives from astragalus root compounds, creating different bioavailability and mechanism profiles.
The copper peptide primarily influences collagen production and wound healing, with less direct telomerase research than Epith
6. Administration Protocols in Research Settings
Investigational protocols typically involve:
-
Cyclical administration (often 10-20 days followed by extended breaks)
-
Subcutaneous or intramuscular injection as primary delivery methods
-
Dosage ranges from 5-10mg daily in human clinical contexts
-
Evening administration to align with natural pineal activity rhythms
Research emphasizes individual variation in response, necessitating careful monitoring in clinical settings. The peptide’s long-term effects remain under investigation, guiding conservative dosing strategies in current studies.
7. Safety Profile and Reported Side Effects
Available research suggests generally favorable tolerability, with noted considerations:
-
Minimal acute toxicity in animal models at therapeutic ranges
-
Potential pineal gland effects requiring careful dosing duration
-
Limited long-term human data necessitating cautious interpretation
-
Reported mild side effects including transient fatigue or sleep pattern changes
Researchers universally recommend medical supervision for any peptide use, emphasizing that safety data remains incomplete despite encouraging preliminary profiles.
8. Current Legal and Regulatory Status
Epithalon exists in a complex regulatory landscape:
-
Research chemical designation in most countries
-
Not FDA-approved for any medical application
-
Compounding pharmacy availability varies by jurisdiction
-
International research continues primarily in Russia and Europe
Potential users must understand that Epithalon lacks approval for disease treatment or anti-aging applications in most regulatory frameworks. Legitimate access typically occurs through clinical research participation or specialized medical compounding where legally permitted.
9. Future Research Directions and Clinical Trials
The scientific community anticipates several developments:
-
Human telomere length studies with rigorous controls
-
Combination therapy research with other longevity interventions
-
Epigenetic mapping to clarify mechanism of action
-
Age-related disease-specific trials for conditions like macular degeneration
Upcoming research will likely focus on validating preliminary findings through randomized controlled trials and identifying specific patient populations that might benefit most from intervention.
10. Practical Considerations for Research Participants
Individuals considering Epithalon research participation should:
-
Consult longevity medicine specialists with peptide experience
-
Complete comprehensive biomarkers before and during intervention
-
Consider combination approaches including lifestyle optimization
-
Maintain realistic expectations given early research stage
-
Prioritize safety monitoring through regular medical supervision
The integrated approach—combining potential peptide interventions with documented longevity practices (nutrition, exercise, sleep optimization)—represents current best practice in the field.
Conclusion: The Cautious Promise of Epithalon
Epithalon research opens fascinating avenues in longevity science, offering glimpses into potential future aging interventions. While preliminary findings intrigue researchers, the peptide requires substantially more investigation before understanding its true therapeutic potential.
Current evidence suggests Epithalon may influence fundamental aging processes, particularly through telomere maintenance mechanisms. However, responsible interpretation demands recognizing the evidence gap between animal studies, cellular research, and proven human applications.
As longevity science advances, Epithalon will likely remain a key research compound for understanding cellular aging. Whether it transitions from research tool to therapeutic intervention depends on forthcoming clinical data and regulatory developments in the evolving field of epigenetic aging modulation
EPITHALON ANTI-AGING PEPTIDE
Epithalon can be easily bought for a reasonable price in sportive pharmacies and other internet shops. The only thing you need to do is to ask for quality check proofs in order not to get scammed or poisoned by low-quality compounds. This is what makes Epithalon so special:
- Since it is a relatively new compound, scientists check and study Epithalon all the time so you can be sure that you will know the latest news about it;
- Epithalon acts fast and has proven effectiveness;
- It has no side effects;
- Epithanon has healing possibilities;
- It also significantly increases energy levels.
At the moment, Epithanon is recognized as the best anti-aging agent. It has a wide range of positive effects on the body.
Epithalon Benefits:
- Stunning anti-aging abilities;
- General health improvement;
- Side effects free;
- Pharmacy grade quality;
- 3rd party lab-tested.
Be the first to review “Epithalon (Anti-Aging) 10mg/vial” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti-Aging
Anti-Aging
Anti-Aging
HGH & Pertides
Anti-Aging








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.